Sometimes, science can surprise us with big discoveries. For a long time, people thought we could only have a certain number of brain cells. After childhood, they believed we couldn’t make any new ones. But something happened in the 1980s that changed this idea completely.
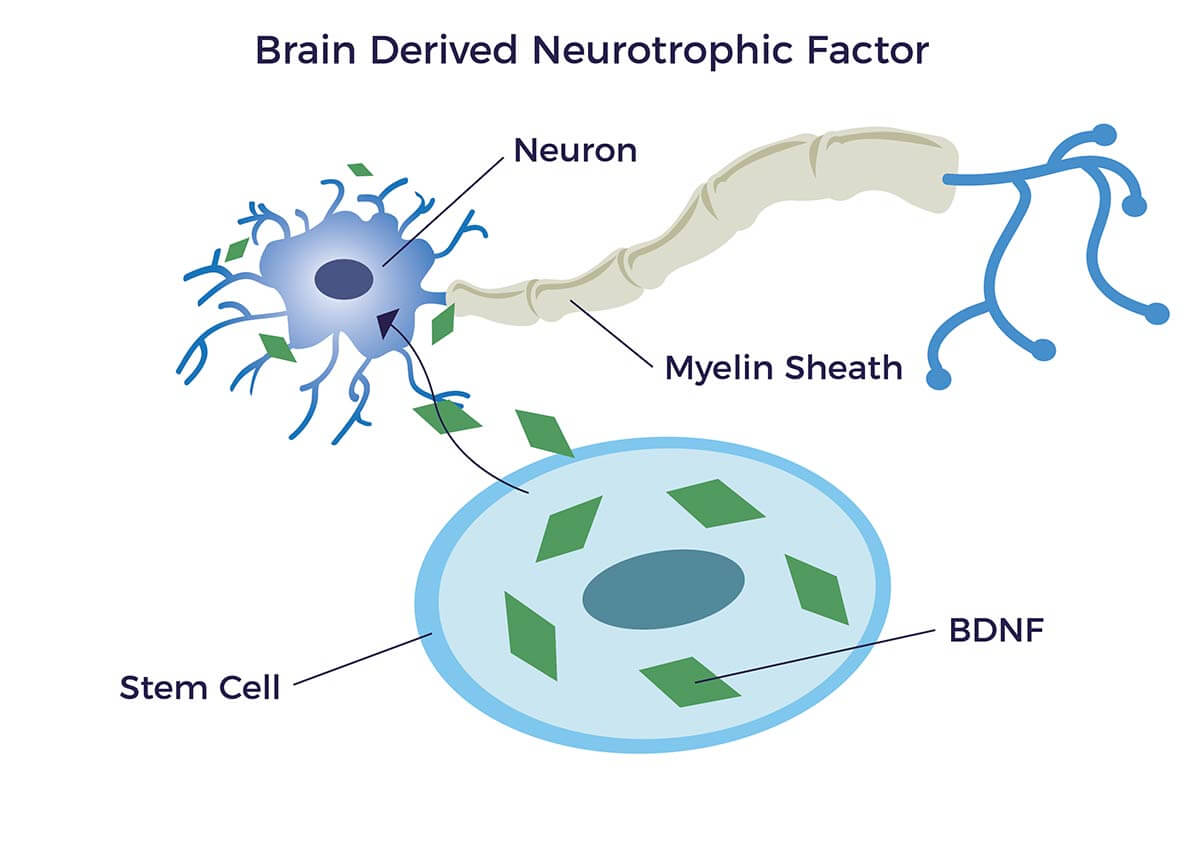
Scientists made an exciting discovery – a protein that could help us grow new brain cells. This protein is like a magical ingredient. It was a real game-changer. The name of this protein is BDNF, short for brain-derived neurotrophic factor.
BDNF is not just any protein. It plays a big role in our brains. It helps make new neurons, improves our memory, and even helps us learn new things. Some scientists even think it might help with brain problems, like Alzheimer’s disease or depression.
So, let’s explore this amazing protein together. We’ll look at what it does, why it’s important, and how it might help us keep our brains healthy. Who knows? Maybe learning about BDNF could even make your brain grow a little bit more!
BDNF: Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor
BDNF is like a superhero for our brains. Its name gives us clues about what it does. “Brain-derived” and “factor” are pretty simple to understand – it’s something that comes from the brain. But the “neurotrophic” part is the real superhero title – coming from the Greek words for “nervous system” and “growth-promoting.”
So, what does our brain superhero do? Well, when scientists first discovered BDNF, they found out it could make brain cells grow. Imagine pouring water on a plant and seeing it sprout new leaves. That’s what BDNF does for our brains.
But that’s not all. BDNF is not just a grower, but also a protector. It takes care of the brain cells we already have. Think of it like a superhero shield, defending our brains from harm. It increases brain flexibility, reduces inflammation, and even fights against depression.
BDNF also has superpowers against aging. It helps protect our brains from diseases that happen when we get older, like Alzheimer’s. Plus, it helps to soften the blow from stress and anxiety on our brains.
Some studies even suggest that BDNF might be linked to how long we live.
So, it’s really important for us to have enough BDNF in our bodies. But that’s not always easy to do. In the next sections, we’ll explore how we can help our bodies make more of this brain superhero.
How To Check Low BDNF levels
When BDNF levels in our bodies are low, we can find out through simple tests using blood or saliva. Researchers have found connections between low BDNF levels and various brain-related problems. Some of these problems include:
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Anxiety, eating disorders, and obsessive-compulsive disorder
- Feeling of burnout
- Dementia
- Depression and thoughts of suicide
- Epilepsy
- Huntington’s disease
- Obesity
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Schizophrenia
- Trouble with sleep
Please remember that just because these problems are connected to low BDNF levels, it doesn’t mean one causes the other. Scientists are still figuring out if low BDNF levels cause these problems, or if these problems cause low BDNF levels. But one thing is sure – the connection between them is strong.
Unhealthy lifestyle choices can also make BDNF levels drop. What we eat can affect our BDNF levels. Foods like fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats can boost BDNF. But too much processed food, especially with lots of sugar and bad fats, can lower BDNF levels.
Stress can also affect our brain health and BDNF levels. When we’re stressed, our bodies make a hormone called cortisol. This hormone can reduce BDNF production, which in turn decreases the growth of new brain cells. This is true for all kinds of stress, like daily stress, occasional big stress events, trouble sleeping from stress, and burnout. There’s even some early evidence suggesting stress during pregnancy might affect a child’s ability to make enough BDNF.
As we get older, our BDNF levels naturally go down. This might be part of the reason why older people have higher risks for problems with thinking and diseases that affect the brain, like Parkinson’s disease and dementia.
Boosting Your BDNF Levels: The Key to Brain Health
There are several ways to boost your BDNF levels, and this can be achieved by adopting healthier habits in terms of exercise, lifestyle, diet, and supplementation.
1. Diet
The type of food you consume significantly influences your BDNF levels. Diets high in sugar and saturated fats, such as the typical Western diet, can be detrimental to your brain health. Conversely, diets rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, like the Mediterranean or Japanese diet, can boost your BDNF levels.
Some specific foods known to boost BDNF production are rich in flavonoids, which are natural compounds that provide numerous health and cognitive benefits. These include foods like black pepper, blueberries, dark chocolate, green tea, olive oil, and turmeric.
Moreover, prebiotic foods, which nourish beneficial bacteria in your gut, like asparagus, bananas, garlic, onions, and tomatoes, are also linked to higher BDNF levels. It’s also worth noting that a correlation has been found between chewing and BDNF synthesis, so opting for foods that require chewing over soups, juices, and smoothies could be beneficial.
2. Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity is a powerful way to enhance your BDNF levels. Whether it’s a brisk walk in the park or an intense gym session, even a single bout of moderate exercise can significantly boost BDNF production. This increase in BDNF aids in fortifying your brain against damage, diseases, and oxidative stress, particularly benefiting the hippocampus, which is crucial for memory and learning.
It’s interesting to note that exercise acts like a switch that turns on the gene responsible for boosting BDNF production. Moreover, exercise can even help counteract some of the negative impacts of sleep deprivation, potentially enhancing BDNF production.
From sprint training and high-impact running to yoga, resistance training, and dancing, all forms of physical activity can help increase your BDNF levels. Just find what works best for you and keep moving!
3. Supplementation
Lastly, taking certain supplements can further enhance your BDNF production. Some herbs and botanicals known to increase BDNF levels include ashwagandha, Asian ginseng, bacopa, cordyceps, and rhodiola rosea.
Remember, before starting any new supplement regimen, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional.
4. Lifestyle
Beyond exercise, your daily lifestyle habits can significantly influence your BDNF levels. One of the simplest ways to enhance your BDNF production is spending more time outdoors. Not only does it lower stress levels (and consequently cortisol), but it also facilitates vitamin D synthesis which in turn stimulates BDNF production.
Listening to or playing music is another lifestyle habit that can boost BDNF levels, as it uplifts your mood and reduces cognitive decline.
High-quality social interactions also play a big role in enhancing BDNF levels. Engaging in meaningful interactions with loved ones, friends, or even pets, can improve your mental health and potentially protect your brain’s long-term health.
Boosting your BDNF levels can be achieved through regular exercise, adopting healthier lifestyle habits, eating a balanced diet, and considering suitable supplements. By taking charge of these aspects, you can promote brain health and optimize BDNF production.
Releted Articles:
Frequently Asked Questions
What is brain derived neurotrophic factor ADHD?
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in relation to ADHD refers to research suggesting that lower BDNF levels may be linked with the occurrence of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, affecting cognitive and behavioral functions.
What is brain derived neurotrophic factor muscle?
BDNF in relation to muscle refers to its role in promoting the survival and growth of neurons that control muscle movement. It also helps mediate the beneficial effects of exercise on brain health.
What is a neurotrophic factor and how does it function?
Neurotrophic factors are proteins that aid the survival, development, and function of neurons. They work by binding to receptors on nerve cells, where they activate cellular pathways that prevent cell death and promote growth and differentiation.
Verdict
Maintaining optimal BDNF levels plays an integral part in your overall brain health. Although a healthcare professional can certainly measure your BDNF levels, it’s empowering to know that you have the tools to bolster them naturally through simple lifestyle changes.
To promote higher BDNF levels, make sure to nourish your body with a well-balanced diet. Get regular exercise, appreciate the great outdoors, and cherish quality time with your loved ones. Immerse yourself in activities that bring you joy and make an effort to manage stress effectively.
Supplementation can also play a pivotal role in boosting BDNF. Consider herbal supplements such as ashwagandha, panax ginseng, and bacopa which are known to support brain health. If you’re already taking them for other reasons, you might be pleasantly surprised to know they’re contributing to your brain health as well.
Remember, the choice to support your brain health is in your hands. By taking a proactive approach, not only will you enhance your BDNF levels, but you’ll also be promoting a healthier, happier you.